In an era where environmental sustainability is paramount, green vehicles have emerged as a pivotal solution to reduce carbon footprints and revolutionize the automotive industry. This comprehensive guide explores the diverse landscape of green vehicles, delving into their environmental benefits, technological advancements, market trends, challenges, and future prospects.
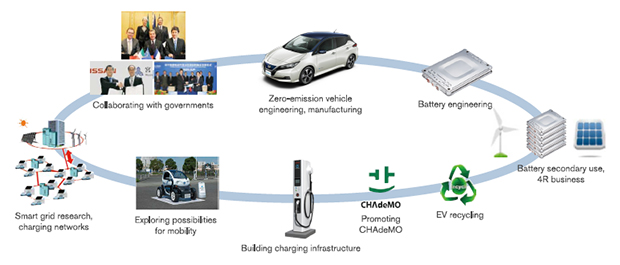
1. Introduction: The Green Vehicle Revolution
Green vehicles represent a transformative shift towards cleaner, more sustainable transportation options. They encompass a range of technologies aimed at minimizing environmental impact while meeting the growing demand for efficient and eco-friendly mobility solutions. This revolution is driven by advancements in battery technology, government incentives, and consumer awareness of climate change.
2. Types of Green Vehicles
Green vehicles come in various forms, each offering unique benefits and capabilities:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Powered solely by electric motors and rechargeable batteries, EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions. They are ideal for urban commuting and short to medium-distance travel, offering quiet operation and lower operational costs compared to internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs): Combine electric motors with traditional gasoline engines. HEVs use regenerative braking to charge their batteries and provide improved fuel efficiency. They are suitable for consumers seeking a balance between fuel savings and reduced emissions without the range limitations of pure electric vehicles.
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs): Similar to HEVs but with larger battery capacities that can be charged from external power sources. PHEVs offer extended electric-only driving ranges, making them versatile for both daily commutes and longer trips.
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles: Use hydrogen gas to generate electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen, emitting only water vapor as a byproduct. These vehicles offer fast refueling times and longer driving ranges, making them suitable for drivers requiring long-distance travel without the need for extensive charging infrastructure.
3. Environmental Benefits
Green vehicles contribute significantly to environmental sustainability:
- Zero Emissions: EVs and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles emit no harmful pollutants during operation, improving local air quality and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. They play a crucial role in mitigating climate change and reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
- Energy Efficiency: Electric drivetrains are more energy-efficient than ICE vehicles, converting a higher percentage of energy from the grid into propulsion. Advances in battery technology continue to increase efficiency and extend driving ranges, making green vehicles more practical and accessible.
- Resource Conservation: By promoting the use of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power, green vehicles reduce the overall environmental impact associated with energy consumption. They contribute to energy security by diversifying energy sources and reducing reliance on finite fossil fuel reserves.
4. Technological Advancements
Continuous innovation in green vehicle technology drives performance and efficiency:
- Battery Technology: Improvements in battery energy density, charging speed, and lifespan enhance the range and affordability of electric vehicles. Next-generation solid-state batteries promise even greater energy storage capacities and faster charging times, further accelerating the adoption of EVs.
- Charging Infrastructure: The expansion of public and private charging networks supports the widespread adoption of EVs. Fast-charging stations reduce charging times and alleviate range anxiety, making electric mobility more convenient and practical for consumers.
- Autonomous and Connected Features: Integration of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and connectivity technologies enhance safety, efficiency, and user experience. Features such as remote vehicle monitoring, over-the-air software updates, and predictive maintenance improve vehicle performance and reduce operational costs.
5. Market Trends and Consumer Adoption
Consumer demand for green vehicles is on the rise, driven by several factors:
- Environmental Awareness: Growing concerns over air pollution and climate change prompt consumers to prioritize eco-friendly transportation options. Government incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, encourage consumers to invest in green vehicles and reduce their carbon footprint.
- Cost Competitiveness: Falling battery prices and economies of scale in manufacturing make green vehicles more affordable and cost-competitive with traditional ICE vehicles. Lower operating costs and reduced maintenance requirements further incentivize consumers to switch to electric and hybrid vehicles.
- Regulatory Environment: Stringent emissions standards and sustainability goals set by governments worldwide push automakers to innovate and develop cleaner, more efficient vehicle technologies. Collaboration between public and private sectors accelerates the adoption of green mobility solutions.
6. Infrastructure Development
Investment in infrastructure is essential to support the growth of green vehicles:
- Charging Networks: Expansion of fast-charging stations in urban areas, highways, and residential communities improves accessibility and convenience for EV owners. Smart charging solutions and interoperable networks enhance the efficiency and reliability of charging infrastructure.
- Hydrogen Refueling Stations: Development of hydrogen refueling infrastructure expands the market for fuel cell vehicles, particularly in regions prioritizing zero-emission transportation solutions. Public-private partnerships and government incentives drive investment in hydrogen infrastructure projects.
- Grid Integration: Integration of renewable energy sources with electric vehicle charging infrastructure promotes sustainable energy practices. Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology enables bi-directional energy flow between EVs and the electric grid, supporting grid stability and optimizing energy use during peak demand periods.
7. Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite the rapid growth of green vehicles, several challenges must be addressed:
- Infrastructure Expansion: The need for continued investment in charging and hydrogen refueling infrastructure to meet growing demand and alleviate range anxiety among consumers.
- Battery Recycling: Development of efficient and sustainable battery recycling processes to minimize environmental impact and maximize the reuse of critical materials.
- Market Competition: Competition from traditional ICE vehicles and alternative fuel technologies poses challenges to the widespread adoption of green vehicles. Continued innovation and cost reduction are essential to maintain market competitiveness.
8. Global Impact and Sustainability Goals
Green vehicles play a crucial role in achieving global sustainability goals:
- Carbon Reduction: Transitioning to electric and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles reduces greenhouse gas emissions and supports efforts to mitigate climate change. Government policies and international agreements promote the adoption of zero-emission transportation solutions.
- Urban Mobility: Green vehicles contribute to sustainable urban development by reducing traffic congestion, improving air quality, and enhancing the quality of life for urban residents. Integrated transportation planning and multi-modal mobility solutions support efficient and equitable access to green mobility options.
- Technological Innovation: Collaboration between automakers, technology providers, and research institutions drives innovation in green vehicle technology, infrastructure development, and energy management. Advances in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and vehicle connectivity pave the way for autonomous and electrified transportation systems.
9. Conclusion: Embracing Sustainable Mobility
Green vehicles represent a paradigm shift towards sustainable transportation solutions, offering environmental, economic, and social benefits. By embracing electric mobility, hydrogen fuel cell technology, and innovative design, society can accelerate the transition to a low-carbon future. Continued investment in technology, infrastructure, and policy support is essential to realize the full potential of green vehicles and ensure a cleaner, greener planet for future generations.
Embrace the infinite possibilities of green vehicles and join the global movement towards sustainable mobility that preserves our environment and enhances the quality of life for all. Together, we can navigate towards a future where zero emissions and sustainable transportation solutions drive positive change and create a more resilient and equitable world.



